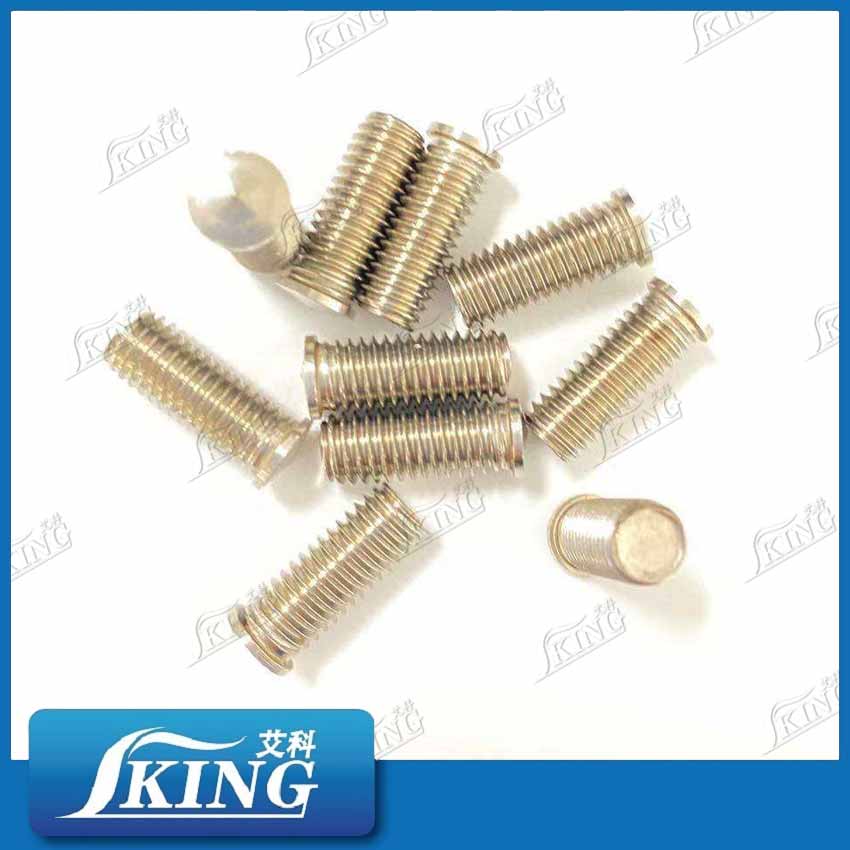
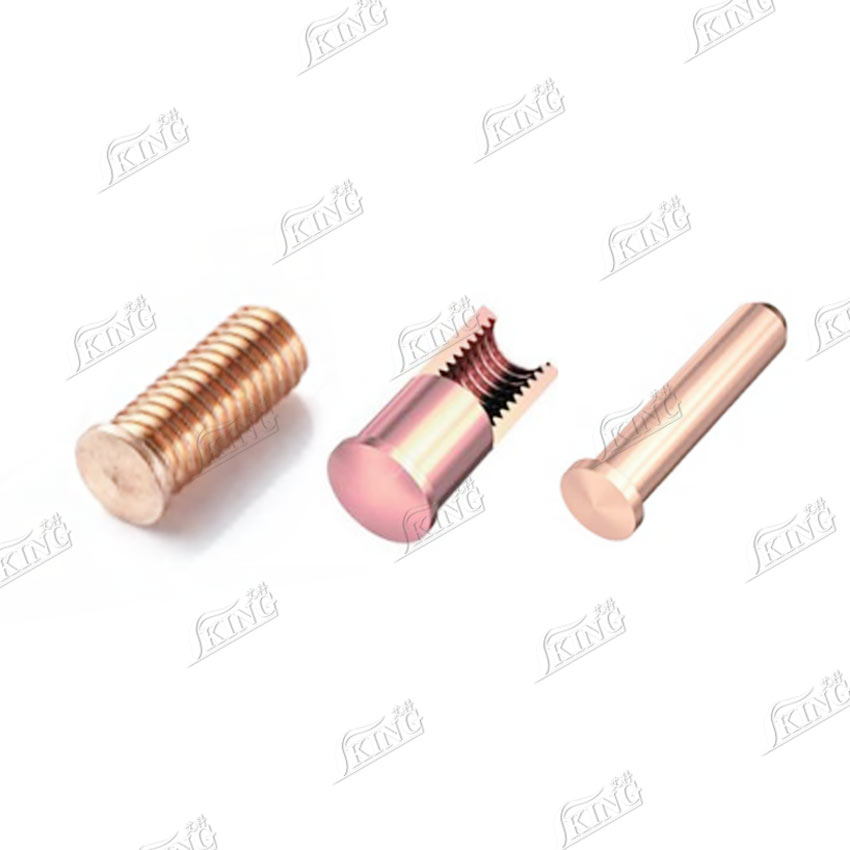
PRODUCT
IKING Short Cycle Welding Studs PS/US/IS Series Carbon Steel/Stainless Steel
Introduction
Short-cycle welding studs are specialized fasteners that utilize a highly efficient electric arc welding process to achieve secure connections. By melting the stud tip and workpiece surface with a short-duration electric arc and applying pressure, a high-strength metallurgical joint is formed. They feature high welding efficiency, strong joint reliability, and convenient operation. The newly released PS, US, and IS series correspond to threaded, unthreaded, and internally threaded studs, respectively, and are available in both carbon steel and stainless steel, comprehensively covering connection needs in various working conditions.
Specification
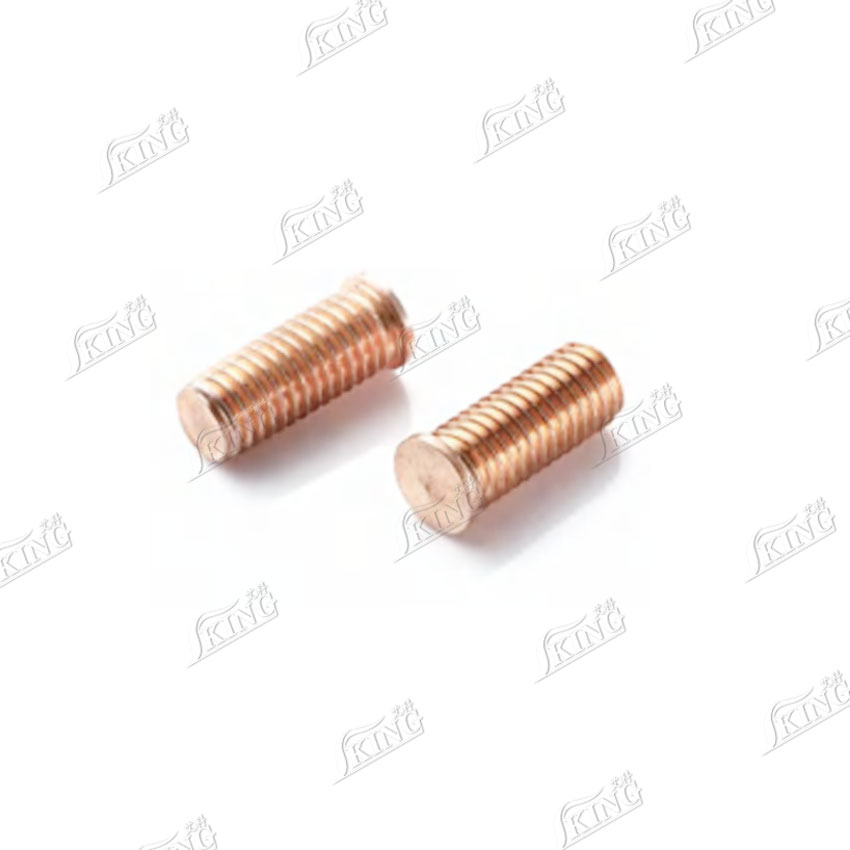
1. Threaded stud with flange (PS)
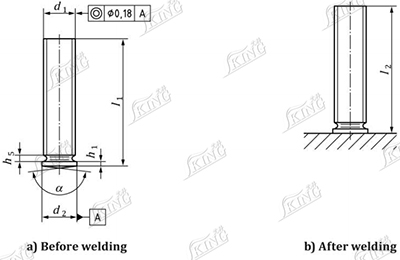
NOTE:l2 (length after welding) depends on l1 and the weld energy.
Dimensions in millimetres
|
d1a |
l1+0.6 |
d2±0.2 |
max.h5 |
h1 |
α±2°b |
|
M3 |
6 |
4 |
0.6 |
0.7 to 1.4 |
166° |
|
M4 |
8 |
5 |
|||
|
M5 |
10 |
6 |
1 |
||
|
M6 |
7 |
||||
|
M8 |
12 |
9 |
1.5 |
0.8 to 1.4 |
|
|
M10 |
16 |
11 |
2.0 |
||
|
a Other types of thread are subject to agreement. |
|||||
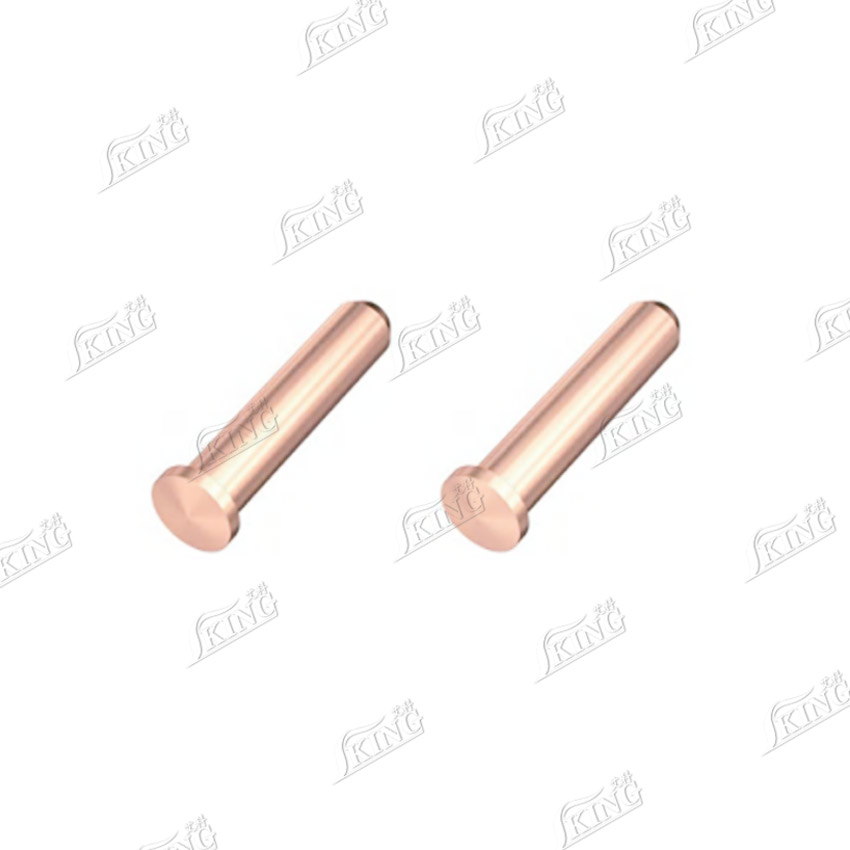
2. Unthreaded stud (US)
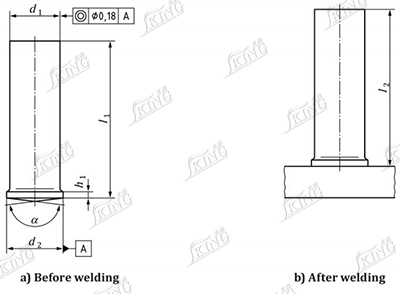
NOTE:l2 (length after welding) depends on l1 and the weld energy.
Dimensions in millimetres
|
d1±0.1 |
l1min+0.6 |
d2±0.2 |
h1 |
α±2°a |
|
3 |
8 |
4 |
0.7 to 1.4 |
166° |
|
4 |
5 |
|||
|
5 |
12 |
6 |
||
|
6 |
7 |
|||
|
7.1 |
15 |
9 |
0.8 to 1.4 |
|
|
8 |
||||
|
a For applications using sheet thicknesses ≥2 mm and welding times >60 ms,the angle,α,may be reduced up to 152°. |
||||
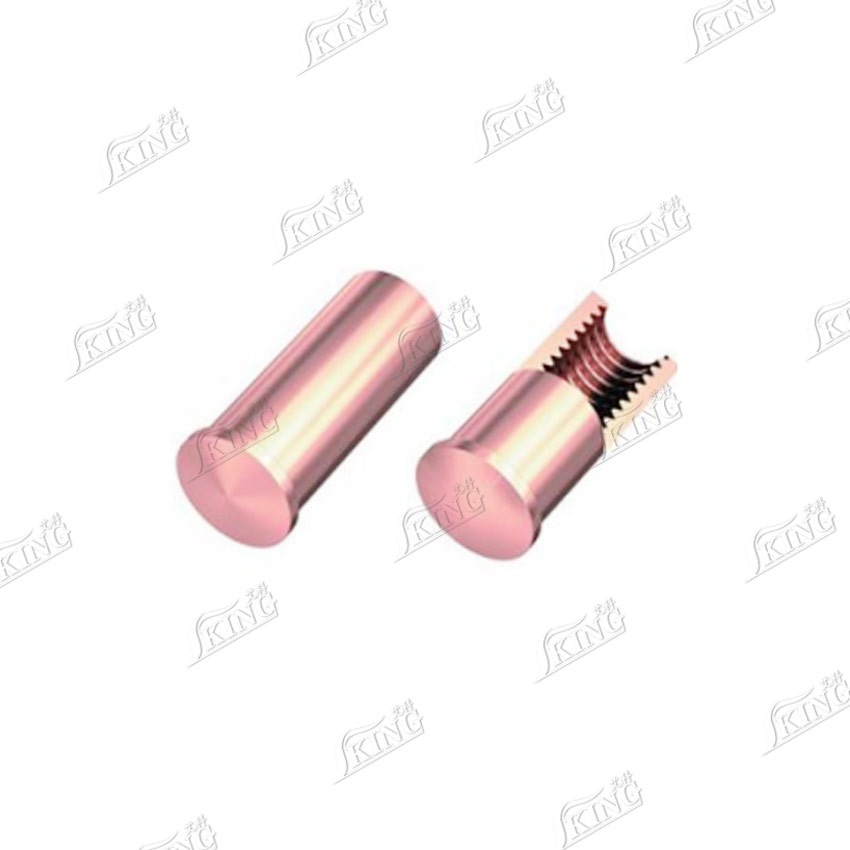
3. Stud with internal thread (IS)
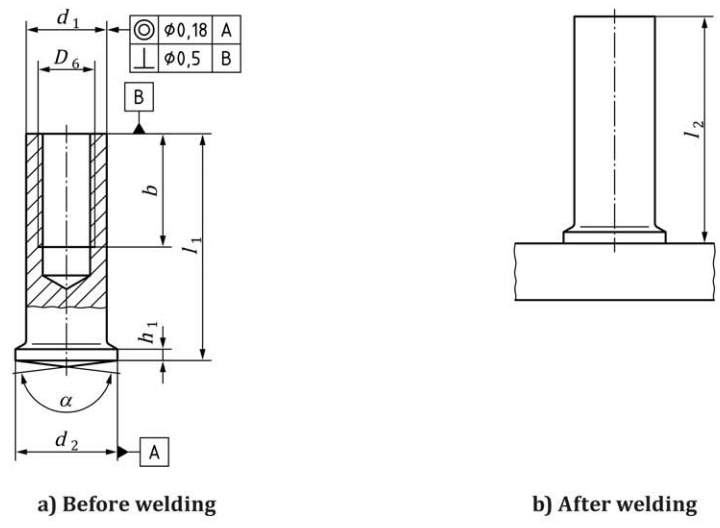
l2 (length after welding) depends on l1 and the weld energy. The depth of the hole shall be at the discretion ofthe manufacturer.
Dimensions in millimetres
|
D6 |
l₁min+0,6 |
bmin + 2P |
d₂ ±0,2 |
d₁ ±0,1 |
h₁ |
α±2°ᵃ |
|
M3 |
10 |
5 |
6.0 |
5.0 |
0,7 to 1,4 |
166° |
|
M4 |
6 |
7.0 |
6.0 |
|||
|
M5 |
9.0 |
7.1 |
0,8 to 1,4 |
|||
|
M5 |
15 |
7.5 |
8.0 |
|||
|
M6 |
9 |
|||||
|
a For applications using sheet thicknesses ≥2 mm and welding times >60 ms, the angle, α, may be reduced up to 152°.) |
||||||
Core Definitions
1. PS Series (Externally Threaded Short-Cycle Welding Studs): The external threads are machined using a rolling process (default conforming to metric or imperial standard thread specifications). The carbon steel version comes standard with copper plating to improve welding performance and corrosion resistance, while the stainless steel version retains the rust-resistant properties of the base material. They can be directly mated with internally threaded connectors for precise assembly.
2. US Series (Threadless Short-Cycle Welded Studs): The threadless design focuses on pure shear force and load-bearing capacity transmission. The end welding base can be flanged or flangeless, with flange diameter and welding base dimensions customizable. The carbon steel material undergoes annealing to optimize weldability, while the stainless steel material is suitable for harsh corrosive environments. The overall structure is simple and provides stable load-bearing capacity.
3. IS Series (Internal Thread Short-Cycle Welded Studs): Features pre-drilled precision threads inside, allowing for secondary connection via external threaded fasteners after welding. This is particularly suitable for scenarios requiring concealed connection points or subsequent disassembly. Material treatment is consistent with the PS series: copper-plated carbon steel and natural stainless steel, ensuring welding reliability and durability.
Material Characteristics
1. Carbon Steel: Utilizes high-quality low-carbon steel such as 4.8 Grade, exhibiting excellent typical tensile strength. Annealing further stabilizes weldability. Standard copper plating reduces welding spatter and improves conductivity; zinc plating, nickel plating, and other surface treatments can also be customized upon request.
2. Stainless Steel Material: Made of stainless steel (304, 316 series), possessing excellent acid and alkali resistance and rust resistance, suitable for humid, outdoor, or corrosive environments such as chemical plants. It also undergoes targeted annealing treatment to ensure uniform weld penetration in short-cycle welding processes.
Advantages
Core Common Advantages
1. High Efficiency and Cost Reduction: Short-cycle welding, less time required; ceramic protective sleeves are not required for diameters ≤ 1/4 inch (protective gas is recommended for improved efficiency in normal operating conditions).
2. Safe and Reliable: Metallurgical joints with deep weld penetration and high shear strength; 360° weld bead visualization for initial inspection; batches can pass the 0.5 pound rubber hammer impact test; bending/torque tests can be performed in special scenarios; conforms to ISO 13918, CE, and other standards.
3. Flexible Adaptability: Surface treatment and thread/flange sizes can be customized; supports flat welding, horizontal welding, and overhead welding (overhead welding becomes more difficult with larger diameters).
4. High Cost-Effectiveness: Copper plating on carbon steel extends service life, while stainless steel utilizes high-cost-performance materials; it is compatible with automation, reducing labor costs and minimizing welding material waste, resulting in a significant overall cost advantage.
Specific Advantages for Each Model
1. PS: High-quality rolled threads offer superior smoothness, strength, wear resistance, and assembly precision; copper plating provides both corrosion resistance and arc stability, reducing welding defects.
2. US: Threadless design reduces processing steps and lowers costs, avoiding thread stress concentration; optional flange base enhances stress stability and expands the stress-bearing area.
3. IS: Concealed internal thread design improves aesthetics; secondary connection facilitates subsequent disassembly and maintenance, improving repair convenience.
Application
Leveraging their high-efficiency welding performance, high-strength connections, and material compatibility, the three major product series are widely used in core fields such as automotive manufacturing, industrial equipment, building structures, and power equipment. The following are detailed descriptions of specific application scenarios:
1. Automotive Manufacturing Industry
As a core application area for short-cycle welding studs, the entire product series is suitable for the automated welding needs of automotive production lines: The PS series is used for fixing components requiring threaded connections, such as chassis brackets, engine mounts, and door hinges; its rolled threads ensure stable assembly of subsequent connected parts. The US series is suitable for purely load-bearing scenarios such as body reinforcement plates and fuel tank brackets; its threadless design simplifies the assembly process. The IS series is used for parts requiring subsequent disassembly and maintenance, such as dashboard brackets and seat rails. The copper-plated carbon steel version is suitable for conventional body parts, while the stainless steel version can be used in areas with high corrosion risks, such as automotive exhaust systems, meeting the automotive industry's welding process specifications for positional tolerances (±1mm) and angular deviations (±2°).
2. The industrial equipment sector
The PS series is used for threaded connections between equipment shells and internal components in the manufacturing of machine tools, construction machinery, and agricultural machinery, such as fixing machine tool protective covers and assembling excavator cab components. The US series serves as a load-bearing support for conveyor belt brackets and equipment base reinforcement. The IS series is suitable for detachable fixing of internal components in distribution boxes and control cabinets. Automated feeding characteristics adapt to batch processing on equipment production lines, improving equipment assembly efficiency, and the welded joint strength meets the vibration and load requirements of mechanical equipment.
3. The building and steel structure sector
The US series is primarily used for connections in steel-concrete composite structures. As shear studs, they effectively connect steel beams to concrete slabs, transferring shear loads and improving the overall stability of the building structure, meeting the stress design requirements of composite structure buildings. The PS series is used for purlin fixing in steel structure workshops and for connecting color steel plate brackets on walls; its threaded connection facilitates subsequent installation and adjustment of the enclosure structure. The stainless steel IS series can be used in corrosive environments such as outdoor stadiums and bridge ancillary structures, ensuring long-term reliability.
4. The field of power and electronic equipment
The PS and IS series are widely used: the PS series is used for threaded fixing of transformer housings and distribution cabinet frames, and the copper plating treatment can improve conductivity and corrosion resistance; the IS series is used for fixing internal wiring terminals of power equipment, and the internal thread design facilitates the disassembly and maintenance of wire terminals; stainless steel products can be used in outdoor power control cabinets, photovoltaic brackets and other scenarios to resist wind and rain erosion.









